Contributed by: MatthewD, FreeTaxUSA Agent, Tax Pro

The gig economy is a flexible labor market where individuals engage in temporary, project-based work. The gig economy has experienced huge growth over the last decade. Companies like Uber, Lyft, Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Amazon Flex, are just a few examples of this trend. Individuals with the freelancer spirit are finding additional financial success by working in this sector of our economy. Many of these businesses require you have a reliable car.
As an example, let’s assume you needed to have your car repaired and rented another vehicle for a few weeks. That rental expense is deductible from your business income, but what form should you use, where on the form would you report it, and how much can you deduct?
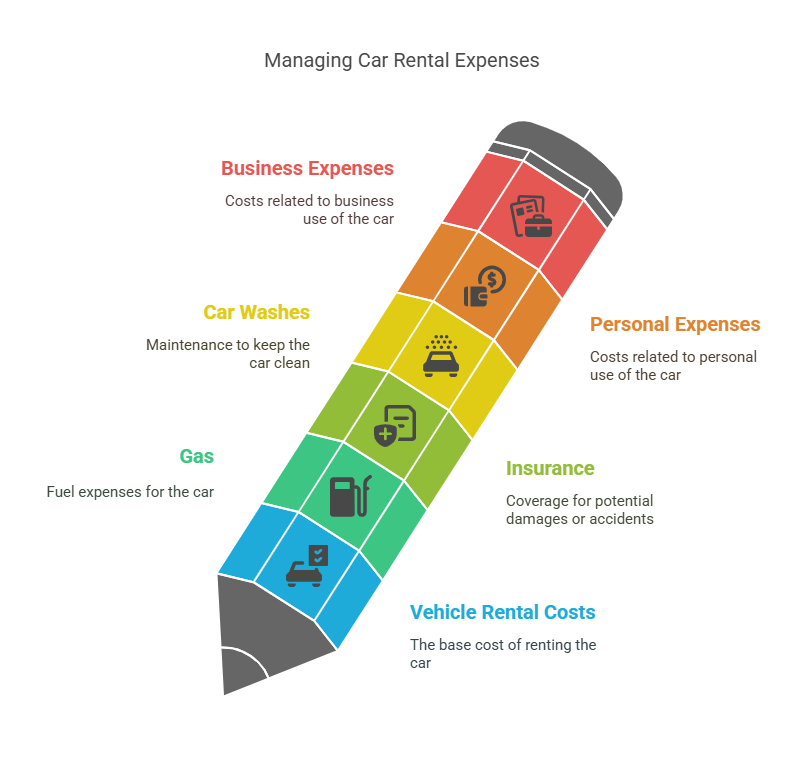
Vehicle rental cost, gas, insurance, and car washes are likely expenses. You’ll also have personal use expenses, so keep track of your business and personal miles to enable you to accurately prorate your business and personal expenses. You’ll have to prorate manually since the software doesn’t perform this function.
Example of reporting business expenses for a rental car
Rental car costs:
- Vehicle rental: $600
- Gasoline: $200
- Vehicle insurance: $125
- Car washes and other supplies: $50
Mileage: Total mileage 1,200 miles. Business 900, personal 300. Business ratio = 75% (900/1,200).
By applying the business ratio of 75% to the costs, here are the prorated business expenses:
- Vehicle rental: $450
- Gasoline: $150
- Vehicle insurance: $94
- Car washes and other supplies: $38
All these expenses will be entered in the Common Expenses section of the Schedule C, not the Vehicle Expenses section.
- Report the car rental as an Equipment Rent expense.
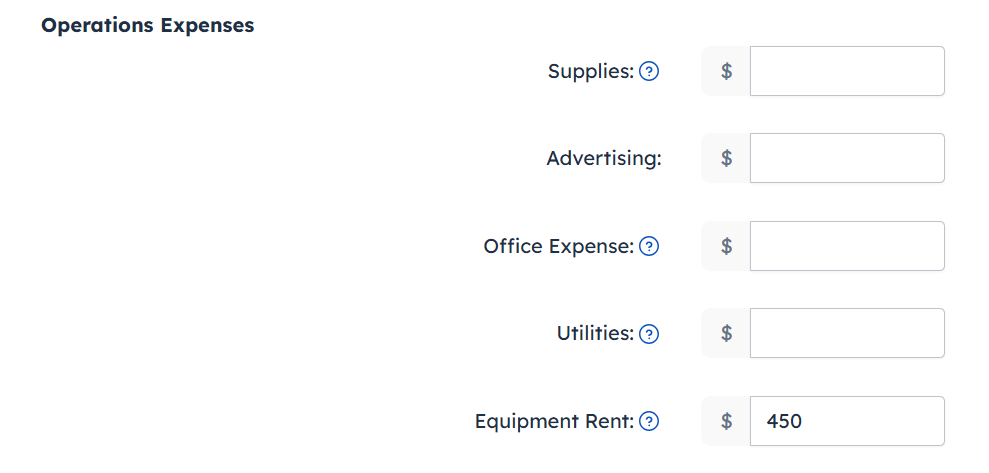
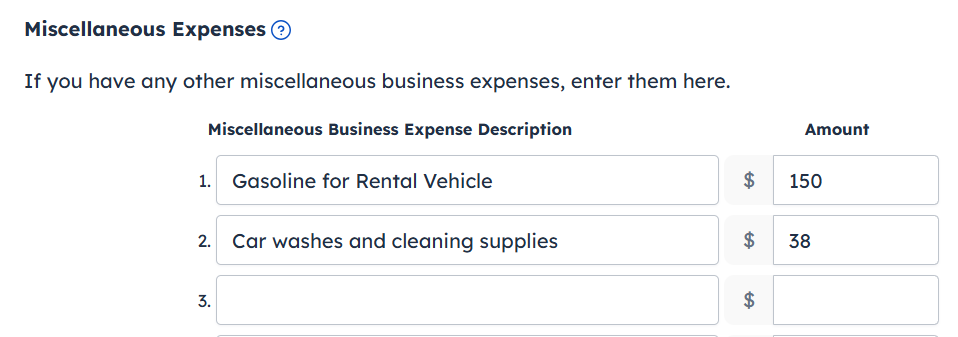
- Report the gasoline cost as a Miscellaneous Expense (include a description).
- Report the car washes and cleaning supplies as a Miscellaneous Expense (include a description).
- Report the vehicle insurance as an Insurance expense.

Summary
Generally, vehicle expenses are entered in the Vehicle Expenses section, but that’s only for vehicles you own or lease. Part of the calculation for using a personal vehicle for business is a depreciation expense, which you can’t take on a rental. Rental car expenses go in the Common Expenses section, and the total expenses must be manually prorated for business and personal use. Only report the business use expenses. Keeping accurate records and recording miles for personal and business use will help you report the expenses properly. Keep in mind that when you rent a car for your business, you must use actual expenses. Rental cars do not qualify for depreciation and the standard mileage option.